Does A Provider Have To Notify Me If A Service Is Not Covered In Network?
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to accept advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Location services on Android
This guide introduces location-awareness in Android applications and illustrates how to get the user's location using the Android Location Service API, as well as the fused location provider available with the Google Location Services API.
Android provides access to various location technologies such as prison cell tower location, Wi-Fi, and GPS. The details of each location technology are abstracted through location providers, allowing applications to obtain locations in the same way regardless of the provider used. This guide introduces the fused location provider, a part of the Google Play Services, which intelligently determines the all-time mode to obtain the location of the devices based on what providers are available and how the device is beingness used. Android Location Service API and shows how to communicate with the organization location Service using a LocationManager. The 2nd part of the guide explores the Android Location Services API using the LocationManager.
Equally a general rule of thumb, applications should prefer to utilise the fused location provider, falling back the older Android Location Service API only when necessary.
Location fundamentals
In Android, no thing what API you choose for working with location data, several concepts remain the aforementioned. This section introduces Location Providers and location-related permissions.
Location providers
Several technologies are used internally to pinpoint the user'south location. The hardware used depends on the type of location provider selected for the job of collecting data. Android uses iii location providers:
-
GPS Provider – GPS gives the almost authentic location, uses the virtually power, and works best outdoors. This provider uses a combination of GPS and assisted GPS (aGPS), which returns GPS information nerveless past cellular towers.
-
Network Provider – Provides a combination of WiFi and Cellular information, including aGPS information collected by cell towers. It uses less ability than the GPS Provider, but returns location data of varying accuracy.
-
Passive Provider – A "piggyback" option using providers requested by other applications or Services to generate location data in an awarding. This is a less reliable but power-saving option ideal for applications that don't crave abiding location updates to work.
Location providers are not always available. For instance, nosotros might want to utilize GPS for our application, but GPS might be turned off in Settings, or the device might not accept GPS at all. If a specific provider is non available, choosing that provider might render zilch.
Location permissions
A location-aware awarding needs access a device's hardware sensors to receive GPS, Wi-Fi, and cellular information. Admission is controlled through advisable permissions in the application's Android Manifest. At that place are ii permissions available – depending on your application's requirements and your choice of API, you lot will want to allow i:
-
ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION– Allows an application access to GPS. Required for the GPS Provider and Passive Provider options (Passive Provider needs permission to access GPS data collected by some other application or Service). Optional permission for the Network Provider. -
ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION– Allows an awarding admission to Cellular and Wi-Fi location. Required for Network Provider ifACCESS_FINE_LOCATIONis not set.
For apps that target API version 21 (Android 5.0 Lollipop) or higher, yous tin can enable ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION and withal run on devices that do not have GPS hardware. If your app requires GPS hardware, you lot should explicitly add an android.hardware.location.gps uses-feature element to the Android Manifest. For more information, see the Android uses-characteristic element reference.
To set the permissions, expand the Properties folder in the Solution Pad and double-click AndroidManifest.xml. The permissions will be listed under Required Permissions:
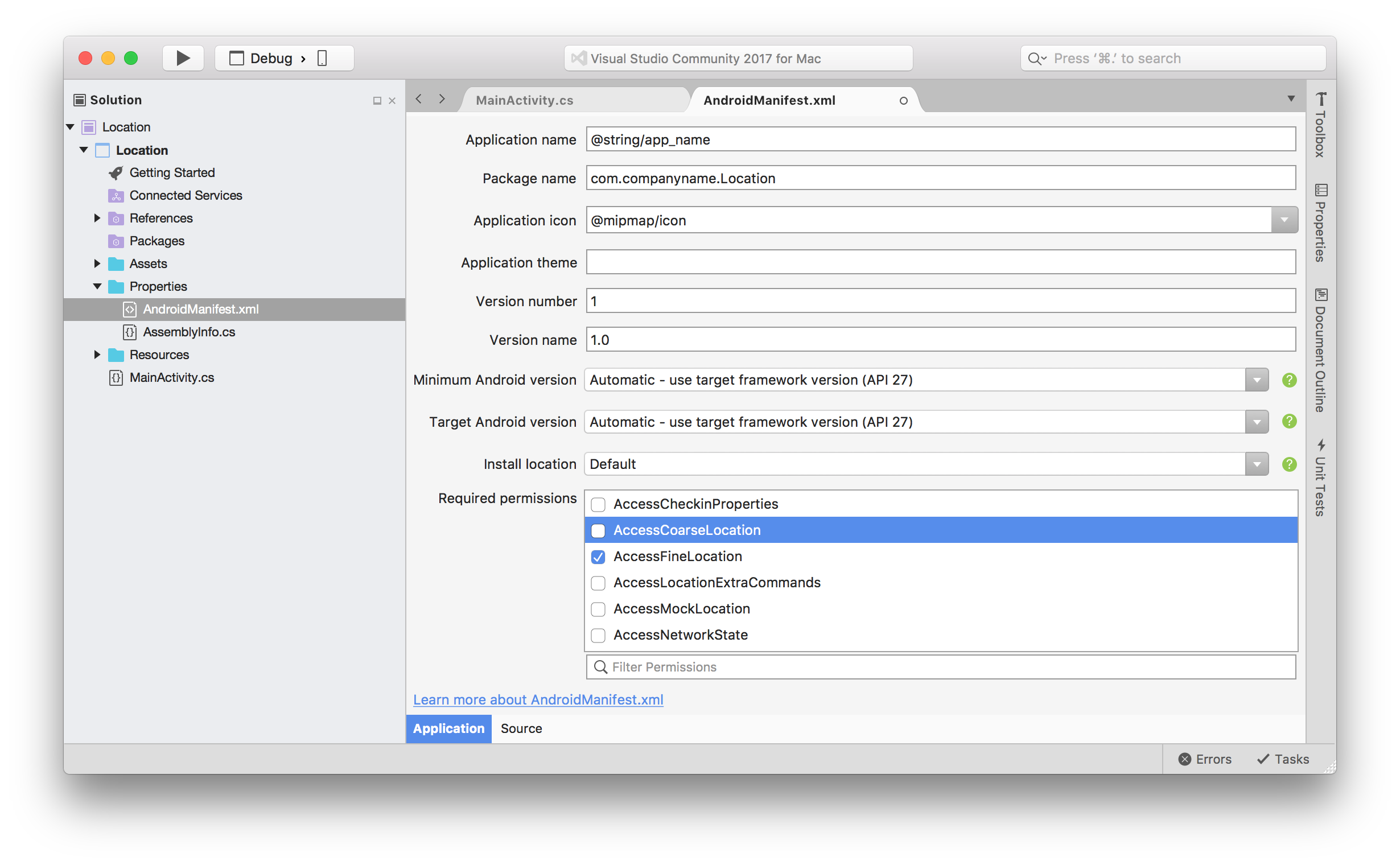
Setting either of these permissions tells Android that your application needs permission from the user in order to admission to the location providers. Devices that run API level 22 (Android 5.1) or lower will ask the user to grant these permissions each time the app is installed. On devices running API level 23 (Android 6.0) or higher, the app should perform a run-time permission check before making a asking of the location provider.
Notation
Notation: Setting ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION implies access to both coarse and fine location data. Yous should never have to set both permissions, only the minimal permission your app requires to work.
This snippet is an example of how to bank check that an app has permission for the ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION permission:
if (ContextCompat.CheckSelfPermission(this, Manifest.Permission.AccessFineLocation) == Permission.Granted) { StartRequestingLocationUpdates(); isRequestingLocationUpdates = true; } else { // The app does not accept permission ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION } Apps must be tolerant of the scenario where the user will not grant permission (or has revoked the permission) and have a manner to gracefully bargain with that state of affairs. Please meet the Permissions guide for more details on implementing run-time permission checks in Xamarin.Android.
Using the fused location provider
The fused location provider is the preferred way for Android applications to receive location updates from the device because it will efficiently select the location provider during run time to provide the all-time location information in a battery-efficient fashion. For instance, a user walking effectually outdoors gets the all-time location reading with GPS. If the user then walks indoors, where GPS works poorly (if at all), the fused location provider may automatically switch to WiFi, which works amend indoors.
The fused location provider API provides a diversity of other tools to empower location-aware applications, including geofencing and activeness monitoring. In this section, we are going to focus on the nuts of setting up the LocationClient, establishing providers, and getting the user's location.
The fused location provider is part of Google Play Services. The Google Play Services parcel must be installed and configured properly in the awarding for the fused location provider API to piece of work, and the device must have the Google Play Services APK installed.
Before a Xamarin.Android awarding tin use the fused location provider, it must add the Xamarin.GooglePlayServices.Location package to the projection. In addition, the post-obit using statements should be added to whatsoever source files that reference the classes described below:
using Android.Gms.Common; using Android.Gms.Location; Checking if Google Play Services is installed
A Xamarin.Android will crash if it tries to apply the fused location provider when Google Play Services is not installed (or out of date) then a runtime exception would occur. If Google Play Services is not installed, so the application should fall back to the Android Location Service discussed in a higher place. If Google Play Services is out of date, then the app could display a message to the user asking them to update the installed version of Google Play Services.
This snippet is an instance of how an Android Activeness tin can programmatically check if Google Play Services is installed:
bool IsGooglePlayServicesInstalled() { var queryResult = GoogleApiAvailability.Example.IsGooglePlayServicesAvailable(this); if (queryResult == ConnectionResult.Success) { Log.Info("MainActivity", "Google Play Services is installed on this device."); return true; } if (GoogleApiAvailability.Instance.IsUserResolvableError(queryResult)) { // Bank check if in that location is a way the user can resolve the issue var errorString = GoogleApiAvailability.Instance.GetErrorString(queryResult); Log.Error("MainActivity", "There is a problem with Google Play Services on this device: {0} - {1}", queryResult, errorString); // Alternately, display the fault to the user. } render fake; } FusedLocationProviderClient
To interact with the fused location provider, a Xamarin.Android application must have an instance of the FusedLocationProviderClient. This class exposes the necessary methods to subscribe to location updates and to retrieve the concluding known location of the device.
The OnCreate method of an Activity is a suitable place to get a reference to the FusedLocationProviderClient, equally demonstrated in the post-obit code snippet:
public form MainActivity: AppCompatActivity { FusedLocationProviderClient fusedLocationProviderClient; protected override void OnCreate(Bundle package) { fusedLocationProviderClient = LocationServices.GetFusedLocationProviderClient(this); } } Getting the last known location
The FusedLocationProviderClient.GetLastLocationAsync() method provides a simple, not-blocking manner for a Xamarin.Android awarding to speedily obtain the last known location of the device with minimal coding overhead.
This snippet shows how to use the GetLastLocationAsync method to retrieve the location of the device:
async Task GetLastLocationFromDevice() { // This method assumes that the necessary run-time permission checks accept succeeded. getLastLocationButton.SetText(Resource.Cord.getting_last_location); Android.Locations.Location location = await fusedLocationProviderClient.GetLastLocationAsync(); if (location == null) { // Seldom happens, but should code that handles this scenario } else { // Practise something with the location Log.Debug("Sample", "The latitude is " + location.Latitude); } } Subscribing to location updates
A Xamarin.Android awarding tin can also subscribe to location updates from the fused location provider using the FusedLocationProviderClient.RequestLocationUpdatesAsync method, as shown in this code snippet:
await fusedLocationProviderClient.RequestLocationUpdatesAsync(locationRequest, locationCallback); This method takes two parameters:
-
Android.Gms.Location.LocationRequest– ALocationRequestobject is how a Xamarin.Android application passes the parameters on how the fused location provider should work. TheLocationRequestholds information such equally how frequent requests should be made or how important an accurate location update should be. For case, an important location request will crusade the device to use the GPS, and consequently more ability, when determining the location. This code snippet shows how to create aLocationRequestfor a location with high accuracy, checking approximately every 5 minutes for a location update (but not sooner than two minutes betwixt requests). The fused location provider will use aLocationRequestas guidance for which location provider to use when trying to make up one's mind the device location:LocationRequest locationRequest = new LocationRequest() .SetPriority(LocationRequest.PriorityHighAccuracy) .SetInterval(sixty * chiliad * 5) .SetFastestInterval(60 * g * two); -
Android.Gms.Location.LocationCallback– In gild to receive location updates, a Xamarin.Android application must subclass theLocationProviderabstract class. This class exposed two methods which maybe invoked by the fused location provider to update the app with location information. This volition be discussed in more particular below.
To notify a Xamarin.Android application of a location update, the fused location provider will invoke the LocationCallBack.OnLocationResult(LocationResult event). The Android.Gms.Location.LocationResult parameter will contain the update location information.
When the fused location provider detects a alter in the availability of location data, it will call the LocationProvider.OnLocationAvailability(LocationAvailability locationAvailability) method. If the LocationAvailability.IsLocationAvailable property returns true, then it tin be causeless that the device location results reported by OnLocationResult are as accurate and as up to date equally required by the LocationRequest. If IsLocationAvailable is faux, and then no location results will exist render past OnLocationResult.
This code snippet is a sample implementation of the LocationCallback object:
public class FusedLocationProviderCallback : LocationCallback { readonly MainActivity action; public FusedLocationProviderCallback(MainActivity activity) { this.activity = activity; } public override void OnLocationAvailability(LocationAvailability locationAvailability) { Log.Debug("FusedLocationProviderSample", "IsLocationAvailable: {0}",locationAvailability.IsLocationAvailable); } public override void OnLocationResult(LocationResult event) { if (result.Locations.Any()) { var location = upshot.Locations.First(); Log.Debug("Sample", "The latitude is :" + location.Latitude); } else { // No locations to piece of work with. } } } Using the Android Location Service API
The Android Location Service is an older API for using location information on Android. Location data is collected past hardware sensors and collected by a organization service, which is accessed in the awarding with a LocationManager course and an ILocationListener.
The Location Service is best suited for applications that must run on devices that practise not have Google Play Services installed.
The Location Service is a special blazon of Service managed by the System. A Arrangement Service interacts with the device hardware and is always running. To tap into location updates in our awarding, we volition subscribe to location updates from the system Location Service using a LocationManager and a RequestLocationUpdates call.
To obtain the user's location using Android Location Service involves several steps:
- Get a reference to the
LocationManagerservice. - Implement the
ILocationListenerinterface and handle events when the location changes. - Employ the
LocationManagerto request location updates for a specified provider. TheILocationListenerfrom the previous stride will be used to receive callbacks from theLocationManager. - Terminate location updates when the application it is no longer appropriate to receive updates.
Location Director
We can access the organization location service with an example of the LocationManager class. LocationManager is a special course that lets us collaborate with the system location Service and telephone call methods on it. An awarding can get a reference to the LocationManager by calling GetSystemService and passing in a Service blazon, equally shown below:
LocationManager locationManager = (LocationManager) GetSystemService(Context.LocationService); OnCreate is a practiced place to get a reference to the LocationManager. It'south a good thought to keep the LocationManager as a grade variable, then that we can telephone call it at various points in the Action lifecycle.
Request location updates from the LocationManager
In one case the application has a reference to the LocationManager, information technology needs to tell the LocationManager what blazon of location data that are required, and how often that data is to be updated. Exercise this by calling RequestLocationUpdates on the LocationManager object, and passing in some criteria for updates and a callback that will receive the location updates. This callback is a blazon that must implement the ILocationListener interface (described in more detail later in this guide).
The RequestLocationUpdates method tells the system location Service that your application would like to start receiving location updates. This method allows you lot to specify the provider, as well equally time and altitude thresholds to command update frequency. For example, the method below requests location updates from the GPS location provider every 2000 milliseconds, and only when the location changes more than 1 metre:
// For this example, this method is part of a class that implements ILocationListener, described below locationManager.RequestLocationUpdates(LocationManager.GpsProvider, 2000, 1, this); An application should asking location updates but as frequently as required for the application to perform well. This preserves battery life and creates a amend experience for the user.
Responding to updates from the LocationManager
Once an application has requested updates from the LocationManager, it tin receive information from the Service by implementing the ILocationListener interface. This interface provides four methods for listening to the location Service and the location provider, OnLocationChanged. The Organisation will phone call OnLocationChanged when the user's location changes enough to qualify as a location modify co-ordinate to the Criteria prepare when requesting location updates.
The following code shows the methods in the ILocationListener interface:
public grade MainActivity : AppCompatActivity, ILocationListener { TextView latitude; TextView longitude; public void OnLocationChanged (Location location) { // called when the location has been updated. } public OnProviderDisabled(string locationProvider) { // chosen when the user disables the provider } public OnProviderEnabled(string locationProvider) { // called when the user enables the provider } public OnStatusChanged(string locationProvider, Availability status, Bundle extras) { // called when the status of the provider changes (there are a multifariousness of reasons for this) } } Unsubscribing to LocationManager updates
In order to conserve system resources, an application should unsubscribe to location updates as soon as possible. The RemoveUpdates method tells the LocationManager to stop sending updates to our awarding. As an instance, an Activity may call RemoveUpdates in the OnPause method so that nosotros are able to conserve ability if an application doesn't need location updates while its Activity is not on the screen:
protected override void OnPause () { base.OnPause (); locationManager.RemoveUpdates (this); } If your application needs to get location updates while in the groundwork, you'll want to create a custom Service that subscribes to the system Location Service. Refer to the Backgrounding with Android Services guide for more information.
Determining the best location provider for the LocationManager
The awarding above sets GPS as the location provider. Notwithstanding, GPS may non be available in all cases, such as if the device is indoors or does not take a GPS receiver. If this is the example, the event is a null return for the Provider.
To get your app to piece of work when GPS is not available, you employ the GetBestProvider method to ask for the best bachelor (device-supported and user-enabled) location provider at application launch. Instead of passing in a specific provider, you can tell GetBestProvider the requirements for the provider - such as accurateness and power - with a Criteria object. GetBestProvider returns the best provider for the given Criteria.
The following code shows how to get the best available provider and apply it when requesting location updates:
Criteria locationCriteria = new Criteria(); locationCriteria.Accurateness = Accuracy.Coarse; locationCriteria.PowerRequirement = Ability.Medium; locationProvider = locationManager.GetBestProvider(locationCriteria, truthful); if(locationProvider != null) { locationManager.RequestLocationUpdates (locationProvider, 2000, ane, this); } else { Log.Info(tag, "No location providers available"); } Note
If the user has disabled all location providers, GetBestProvider will return naught. To see how this lawmaking works on a real device, be sure to enable GPS, Wi-Fi, and cellular networks under Google Settings > Location > Mode equally shown in this screenshot:

The screenshot below demonstrates the location awarding running using GetBestProvider:

Proceed in mind that GetBestProvider does not change the provider dynamically. Rather, it determines the best bachelor provider in one case during the Activity lifecycle. If the provider status changes afterward it has been set, the application volition require additional code in the ILocationListener methods – OnProviderEnabled, OnProviderDisabled, and OnStatusChanged – to handle every possibility related to the provider switch.
Summary
This guide covered obtaining the user'due south location using both the Android Location Service and the fused location provider from Google Location Services API.
- Location (sample)
- FusedLocationProvider (sample)
- Google Play Services
- Criteria Class
- LocationManager Class
- LocationListener Class
- LocationClient API
- LocationListener API
- LocationRequest API
Source: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/xamarin/android/platform/maps-and-location/location
Posted by: kisertany1937.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Does A Provider Have To Notify Me If A Service Is Not Covered In Network?"
Post a Comment