Which Of The Following Is Not Considered A Characteristic Of Service
Half-dozen key distinguishing characteristics of services are as follows: a. Intangibility b. Inseparability c. Variability d. Perishability eastward. Heterogeneity f. Lack of Ownership.
1. Intangibility :
Services cannot more often than not be seen, tasted, felt, heard or smelt before being bought. The potential customer is unable to perceive the service before (and sometimes during and after) the service delivery. For many customers of car repair, for example the service is totally intangible – they often cannot come across what is being done and many indeed are unable to evaluate what has been washed.
Implications:
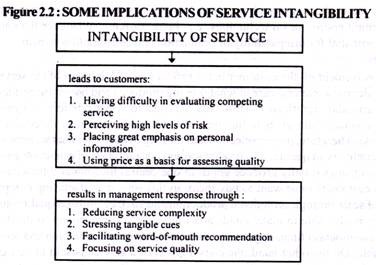
Intangibility presents bug in that consumer may feel difficulty in knowing and understanding what is on offer earlier, and even after, receipt of the service. The challenge for the service provider is to determine the extent of intangibility and the management activity required to brand the service more tangible (Figure two.two). The kickoff task implies resort to some form of measurement, and the 2d task involves the provision of tangible evidence, e.thou. a brochure to help consumer agreement of the service.
Pure services have no tangible properties which can be used by consumers to verify advertizing claims before the purchase is fabricated. The intangible process characteristics which define services, such as reliability, personal care, attentiveness of staff, their friendliness, etc., can only exist verified in one case a service has been purchased and consumed.
Intangibility has a number of important marketing implications. The lack of concrete evidence that intangibility implies increases the level of uncertainty which a consumer faces when choosing between competing services.
An important part of a services marketing program will therefore involve reducing consumer dubiety past such means as adding physical evidence and the development of strong brands. It is interesting to notation that pure goods and pure services tend to move in opposite directions in terms of their general approach to the upshot of tangibility. While service marketers seek to add tangible prove to their production, pure appurtenances marketers often seek to augment their products past adding intangible elements such as after-sales service and improved distribution.
Testify Cosmos:
The power to flick a service may exist assisted by the service system providing something tangible. This may be in the grade of tangible show, e.g. computerized representation of hairstyles or a tangible possession, e.g. a university prospectus. The aim would be to assist the potential customer grade expectations earlier using the service. As, tangible evidence and possessions could help customer judgment of the service during and afterwards usage.
ii. Inseparability :
In that location is a marked stardom between concrete goods and services (Figure two.iii) in terms of the sequence of production and consumption.

Whereas goods are kickoff produced, and and so stored, and finally sold and consumed, services are first sold, then produced and consumed simultaneously. For the production of many services (due east.g. counselling, museums, hairdressing, track travel, hotels) the customer must be physically present.
Some services may be produced and delivered in circumstances where the customer's presence is optional, due east.g. carpet cleaning, plumbing. Other services may rely more on written advice, e.thou. distance learning course, or on technology, e.m. domicile banking. Whatever the nature and extent of contact, the potential for inseparability of production and consumption remains.
Implications:
The interest of the customer in the product and commitment of the service ways that the service provider must exercise care in what is existence produced and how it is produced. The latter task will be of particular significance. How teachers, doctors, bank tellers, lawyers, machine mechanics, hairdressers conduct themselves in the presence of the customer may determine the likelihood of repeat business.
Therefore, proper selection and training of customer contact personnel are necessary to ensure the delivery of quality. The production and consumption of a tangible good are two discrete activities. Companies usually produce goods in 1 central location and and then transport them to the place where customers most want to buy them. In this way, manufacturing companies can achieve economies of scale through centralized product and accept centralised quality-command checks.
The manufacturer is also able to make goods at a time which is user-friendly to itself, so make them available to customers at times which are convenient for them. Production and consumption are said to be separable.
On the other hand, the consumption of a service is said to exist inseparable from its ways of product. Producer and consumer must unremarkably interact in order for the benefits of the service to be realized – both must meet at a fourth dimension and a place which is mutually convenient in social club that the producer can directly pass on service benefits.
In the extreme case of personal care services, the customer must be present during the entire production process – a doctor cannot provide a service without the involvement of a patient. For services, marketing becomes a means of facilitating circuitous producer – consumer interaction, rather than being but an exchange medium.
Inseparability occurs whether the producer is man, equally in healthcare services, or a machine, as in the instance of a banking concern ATM auto. The service of the ATM machine can just be realized if the producer and consumer collaborate. In some cases, it has been possible to split up service product and consumption, peculiarly where there is little need for personal contact.
Inseparability has a number of important marketing implications for services (Effigy ii.4). First, whereas goods are generally start produced, then offered for auction and finally sold and consumed, inseparability causes this process to be modified for services. These are mostly sold commencement, then produced and consumed simultaneously. Second, while the method of goods production is to a large extent (though past no ways always) of fiddling importance to the consumer, product processes are critical to the enjoyment of services.
Some implications of service inseparability:

3. Variability :
An unavoidable consequence of simultaneous production and consumption is variability in performance of a service. The quality of the service may vary depending on who provides it, as well as when and how it is provided. 1 hotel provides a fast efficient service and some other short distance abroad delivers a tedious, inefficient service. Within a particular hotel, one employee is courteous and helpful while another is arrogant and obstructive. Even within one employee there can exist variations in operation over the course of a day.
Implications:
Reducing variability involves determining the causes. It may exist due to unsuitable personality traits in an employee which are very difficult to discover at the selection stage. There is cipher much that tin can be done well-nigh this except hope that the employee decides to finish his employment. However, in that location may exist good audio reasons for variations in functioning. For example, it could be due to poor preparation and supervision, lack of communication and information and generally a lack of regular support.
Some take argued for a replacement of labour with automation and a production line approach to service operations. This would mean a reduction in employee discretion and an increase in standardization of procedures. The performance of pizza restaurants is put forrad every bit an ideal model of vice industrialization.
For services, variability impacts upon customers in terms not merely of outcomes merely also of process of production. Information technology is the latter point that causes variability to pose a much greater problem for services, compared to goods. Because client are usually involved in the production process for a service at the same time as they consume it, it tin can be difficult to carry out monitoring and control to ensure consistent standards.
The opportunity for pre-commitment inspection and rejection which is open to the goods manufacturer is non commonly possible with services-the service must usually be produced in the presence of the customer without the possibility of intervening quality command. Particular bug tin occur where personnel are involved in providing services on a i-to-one basis-such as hairdressing – where no like shooting fish in a barrel method of monitoring and control is possible.
The variability of service output can pose problems for brand building in services compared to tangible goods – for the latter it is usually relatively easy to incorporate monitoring and a quality command procedures into product processes in social club to ensure that a brand stands for a consistency of output. It is ofttimes difficult to reach standardization of output in services.
4. Perishability :
Services cannot exist stored for afterward auction or use. Hotel rooms not occupied, air line seats non purchased, and college places not filled cannot exist reclaimed. Every bit services are performances they cannot be stored. If demand far exceeds supply information technology cannot be met, every bit in manufacturing, past taking goods from a warehouse. As, if capacity far exceeds demand, the revenue and/or value of that service is lost.
Implications:
Fluctuations in need characterize service organizations and may pose problems where these fluctuations are unpredictable. Strategies demand to be developed for producing a better match between supply and demand. Services differ from goods in that they cannot be stored. A producer of cars which is unable to sell all its output in the current period can carry forrad stocks to sell in a subsequent one.
The only significant costs are storage, financing and the possibility of loss through obsolescence. In contrast, the producer of a service which cannot sell all is output produced; in the electric current catamenia has no chance to carry it forward for sale in a subsequent one. An airline which offers seats on ix.00 a.thou. flying from Bombay to Delhi cannot sell whatever empty seats once the aircraft has left.
The service offer disappears and spare seats cannot be stored to meet a surge in demand which may occur at, say. 10.00 a.m. The perishability of services results in greater attention having to be paid to the management of demand by evening out peaks and troughs and in scheduling service production to follow this pattern as far equally possible. Pricing and promotion are two of the tools ordinarily adopted to tackle this problem.
5. Heterogeneity :
Fifty-fifty though standard systems may be used, for example to handle a flying reservation, to volume in a customer's car for service or to quote for insurance on his life. Each 'unit' of a service may differ from other 'units'. Franchise operations, attempt to ensure a standard of conformity, but ultimately information technology is difficult to ensure the same level of output in terms of quality. From the customers' viewpoint besides information technology is hard to judge quality in advance of purchase; although this element as well applies to some product marketing.
Capacity level should be available on cope with surges in demand before service levels suffer. Equally, attention has to be given in times of low levels of usage on whether spare capacity will lie idle or whether curt-term policies (e.one thousand. differential pricing, special promotions), will be adopted to fifty-fifty out fluctuations in demand. Some illustrations of programmes that may be adopted to compensate for fluctuating need are shown in Table 2.2.

half-dozen. Lack of ownership :
Lack of ownership is a bones difference between a service manufacture and a production manufacture because a customer may simply have access to or employ of a facility (e.g. a hotel room, a credit card). Payment is for the utilize of, access to or hire of items. With the sale of a tangible expert, barring restrictions imposed say by a hire purchase scheme, the buyer has full use of the production.
A summary of these characteristics of services with some implications is shown in Table 2.3.
Table 2.iii: Some constraints on the management of services and ways of overcoming them: 
Which Of The Following Is Not Considered A Characteristic Of Service,
Source: https://www.yourarticlelibrary.com/services/services-characteristics-6-key-distinguishing-characteristics-of-services/34008
Posted by: kisertany1937.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Of The Following Is Not Considered A Characteristic Of Service"
Post a Comment